What is REST?
Nowadays we are using REST integration
interface to interact with external systems through web service in Pega,
basically to make calls between machines.
REST stands for Representational State Transfer Protocol.
What is REST in Pega?
Pega is proving a service (response)
to the external system by processing the request received from an external system.
Basically, we will receive a
request from external system/machine to Pega, Pega will process that request
and provides a response back to an external system.
 |
| Add caption |
The request will be in different types
XML/JSON. Let’s consider the request type is JSON.
JSON - JavaScript Object Notation, it is like standard file format and
interchange format, a layman can understand this format. Below is the Sample JSON
request, using to create a case for Instawit
customers for their online clients based on the account number.
Request
JSON
{
"serviceHeader":
{
"channelID":
"IW-Online",
"userId":
"iw12345",
"serviceName":
"IW"
}, "serviceBody": {
"serviceRequest":
{
"context":
{
"custInfo":
{
"Name"
: "IWcutomer
"Description"
: "Instant Pega Knowledge",
"AccountNumber"
: "ABC15797531" }
}} } }
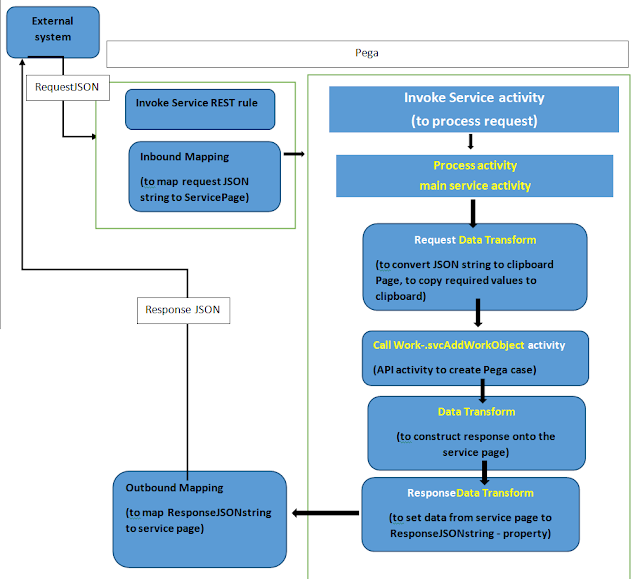
How Pega will process this JSON request, see simple data flow below:
Response
JSON: will look like
{
"serviceHeader":
{
"channelID":
"IW-Online",
"userId":
"iw12345",
"serviceName":
"IW"
"statusMsg":"SUCCESS",
"statusCode":"00"
}, "serviceBody": {
"serviceResponse":
{
"context":
{
"custInfo":
{
"Name"
: "IWcutomer
"Description"
: "Instant Pega Knowledge",
"AccountNumber"
: "ABC15797531"
“caseId” : “IW-57”}
}
} } }
How do I create a service rest in PEGA?
What is the PEGA service package?
Let’s see the technical things behind this
process: Service Package
1.
We should have a service package
rule, it is the heart of all Service rules like
SOAP Rule-Service-SOAP
HTTP Rule-Service-HTTP
SAP
Rule-Service-SAP
REST Rule-Service-REST
2. The service package is a Data
instance (Data-Admin-ServicePackage).
3.
What is the processing mode,
stateless or Stateful?
Stateless: From the requestor pool, if any requestor can run the services
defined in this service package, even if the requestor is processed earlier.
Stateful: otherwise chooseStateful.
4.
Service access group, this is a
required field.
We need to provide access
group value for the service package rule, basically to provide the context, and
Rule resolution will sue this access group to find and execute correct Service
rule.
5.
Requires authentication check
box: If authentication is required for the service request select the check
box. If checked, will be having Basic, OAuth 2.0, and custom(where we can create
authentication service rule)
6.
Suppress Show-HTML check box:
to skip the Show-HTML step in any
activity, which is executing in any service rule that references this service
package.
7.
Methods tab will show all the
Service (REST, SOAP, HTML, and SAP) rules which are using this service package.
8.
Pools Tab: requestors pool for
the services in this service package, like a requestor’s bench.
a.
Specify how many requestors can
be in Idle in this pool to perform the services from this package.
b.
Specify how many active
requestor we can have in this pool to perform the services from this package.
c.
Specify how much time (in
seconds) should the system waits for each requestor to return to this pool when a
service request arrives.
We have the service package ready and it
has our Service REST rule in Methods section drop down in context tab of
service package rule.
1. The external system will send a
request (JSON format), our service package will receive and locate all the
rules based on the access group and will assign a requestor to perform this
service from the requestor pool.
2.
Service REST rule will be
invoked and will see the Service tab, where we have Page class and Page Name.
Let’s say Page class is
“IW-Work-XYZ” and Page name like “CaseReqPage”.
3.
Service REST will be executing
on the “CaseReqPage’ of class “IW-Work-XYZ” and Service activity will be
invoked by using the same class.
4.
Pega will do Inbound Mapping
where Request JSON string will be copied to “CaseReqPage” to a property identified in “Map to key” the field in Request tab.
5.
Service activity will be
invoked as identified from the POST method tab.
6.
This is the Service activity
were actually processing the request and response.
a.
Use Data Transform to map the
inbound requests to the clipboard.
b. We have requested as JSON string in the CaseReqPage, we can use pega
OOTB function to convert JSON string to clipboard Page ----remember we are on the CaseReqPage context only…
c.
Pega will convert JSON string
to clipboard page by using @(Pega-RULES:Page).pxConvertStringToPage(tools,
Primary.Service, CaseRequestPage.RequestJSONString,"json")
d.
Once the conversion is a success we
can map required or necessary properties to “CaseReqPage”, conversion page will
look like below:
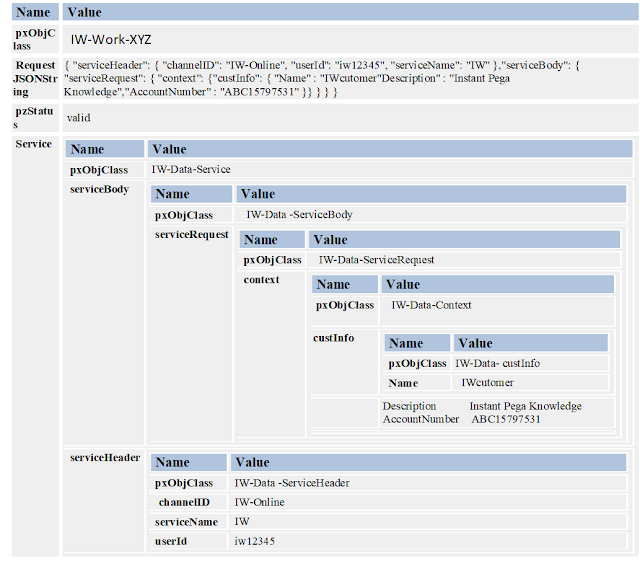
a.
We can copy whatever the JSON
properties required on to the CaseReqPage, we can do that here.
b.
We will identify the pyWorkPage
class by using Decision table or Data transform or DCR (dynamic class
referencing) -----context will be pyWorkPage----
c.
We will call the OOTB Call
Work-.svcAddWorkObject activity to create the case using values from
CaseReqPage. We need to pass parameters to this activity
d.
svcAddWorkObject will create
the Case to the particular case type based on the class of pyWorkPage.
e.
Pega will create a case and will
enter into the Particular Case type and perform the stages and will return to
the svc activity.
f.
We will have all the case type
related values onto the pyWorkPage.
1.
Main service activity, will call
another data transform to construct the response by using pyWorkPage and other
pages. ----context will be CaseRegPage-----
2.
Once, response construction is
complete, we need to map the response values to a JSON Response string.
3. Mapping of outbound value will begin here, where we are setting all
our response pages into a property (string).
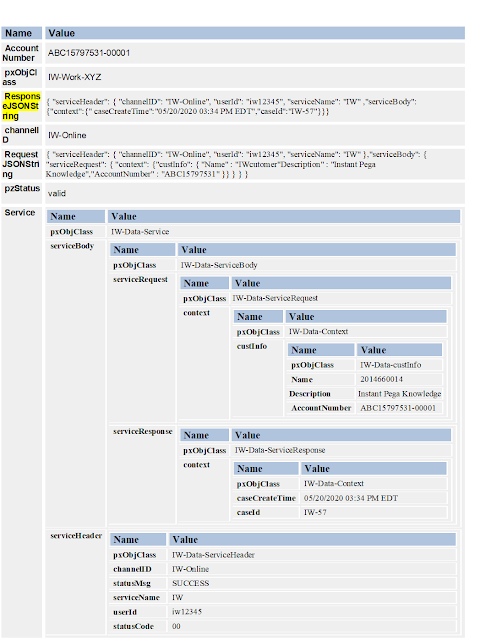
Final
CaseReqPage may look like below:

nice information, well explained.
ReplyDeleteWow thaq for giving this valuable information
ReplyDeleteIt is very useful to us. Thank you so much for this valuable information
ReplyDeleteWhat is the access role used while configuring service rest
ReplyDeleteIn Pega, when configuring a Service REST, the access role used is typically the Service Role. This role is granted to users or applications that will interact with the REST service. It ensures that only authorized entities can access and invoke the service.
DeleteThe specific steps to configure access roles for a Service REST are:
Define a Service Role: This role is associated with the access required for the service. It ensures that the appropriate users or systems can invoke the REST service.
Assign the Service Role: In the Service REST rule, under the Security tab, you can assign the specific access role that should have permission to invoke the service.
Configure Authentication: You can also define authentication settings such as Basic Authentication or OAuth, ensuring that only users or systems with the correct credentials can access the service.
This role-based access helps secure your Service REST by limiting who can interact with it.